Initialize your First Project
Start a New Project
With your tooling properly set up in the previous chapter, you can now start with setting up your Django project.
Create a new folder for your project.
And open the folder in your editor of choice, such as VSCode
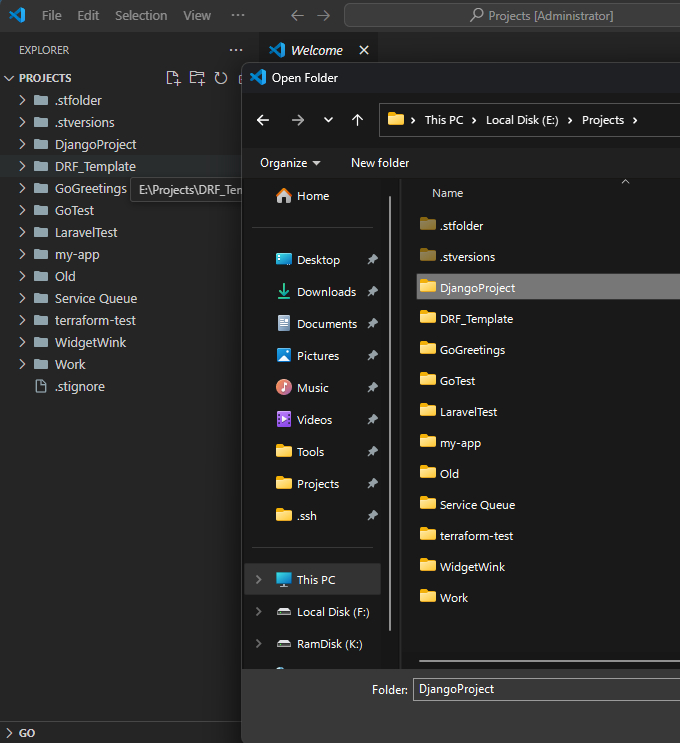
Create a new Python virtual environment with Pipenv by running pipenv shell
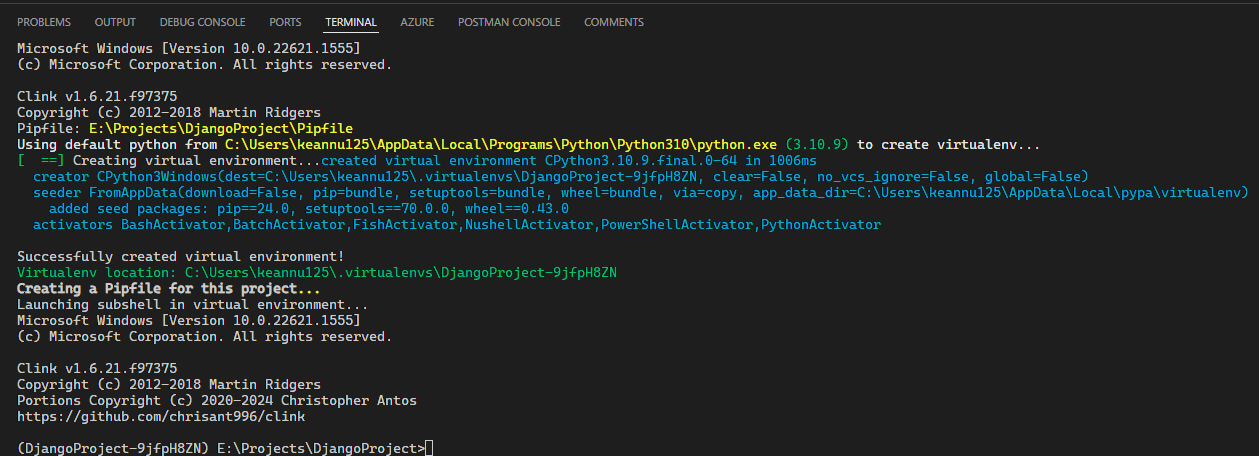
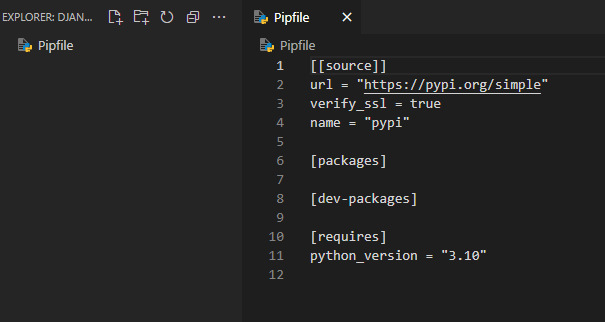
This will create a Pipfile in your project folder. This will track what packages you install in your virtual environment
 I highly suggest you install the Python VSCode extension at this step to help with your developer experience
I highly suggest you install the Python VSCode extension at this step to help with your developer experience
Initialize Git
When working on software projects such as Django, you will need to be able to track small changes. We'll be using Git for that
We previously installed Git, now's the time to use it. In your terminal, run the command git init
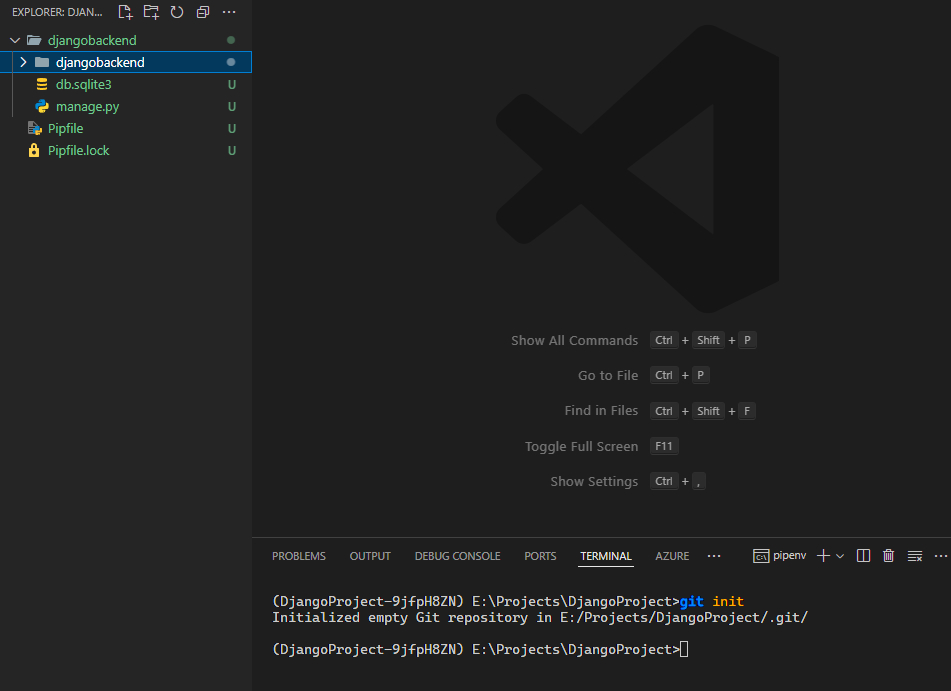
If successful, this will create a hidden .git folder in your project
There are some files in your projects that won't need to be tracked for changes (database files, and passwords!)
Download the .gitignorefile provided here or from here below and drop it into your root project folder.
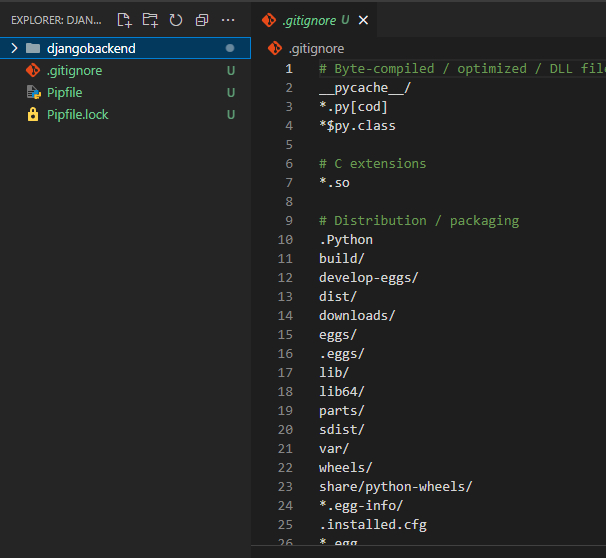
Don't forget to rename it to .gitignore. Take note of the dot before the filename!
You can also choose to search for your own .gitignore template online for Django or Python which will work fine too.
Select your Interpreter
Since you're using a virtual environment such as Pipenv, you will need to specify it to be used rather than the default Python installation
Press CTRL + Shift + P to open the VSCode menu and type in Select Interpreter.
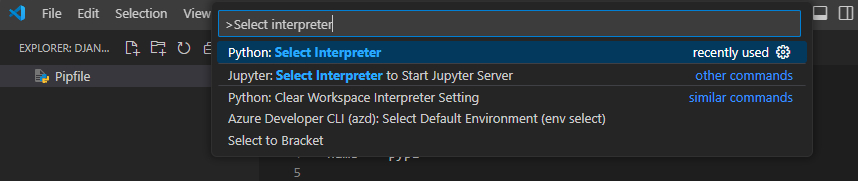
Select the virtual Python environment you created earlier (eg. the one created from pipenv shell)
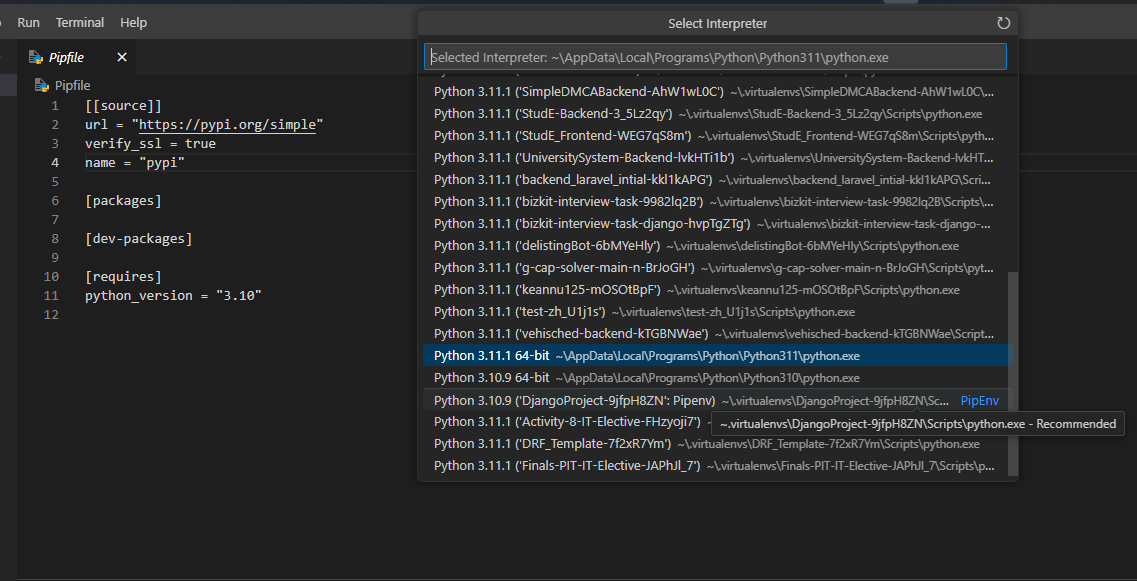
Install Dependencies and Packages
To use Django, you'll need to install Django!
On your current project's code editor, open a terminal or command line and type in the command
pipenv install django djangorestframework
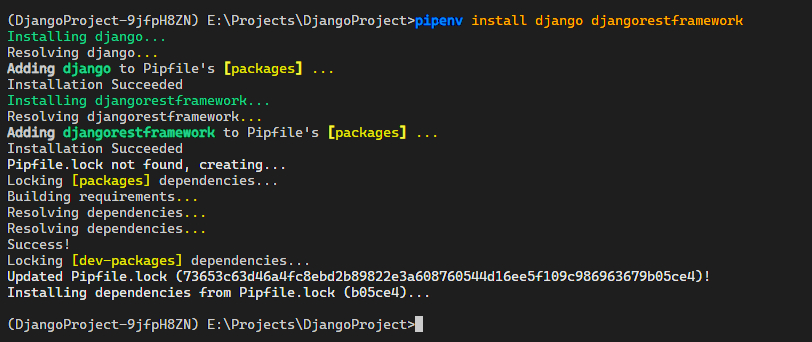
This will update your Pipfile and create a Pipfile.lock to reflect the installed packages
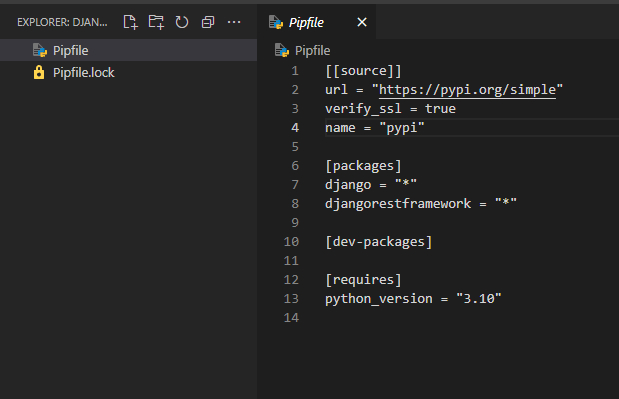
Initialize the Project
In your code editor's terminal or command prompt, run the command
django-admin startproject PROJECT\_NAME
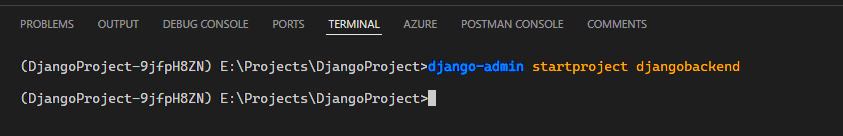 ](https://bookstack.06222001.xyz/uploads/images/gallery/2024-09/i5bimage.png)
](https://bookstack.06222001.xyz/uploads/images/gallery/2024-09/i5bimage.png)
Be sure to replace it with your own project name! I named mine djangobackend.
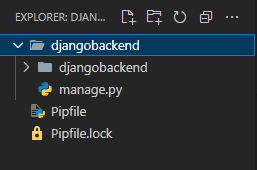
A new directory will be created, containing your Django project's files
[
Change your directory in the terminal to the folder just created eg. cd PROJECT\_NAME
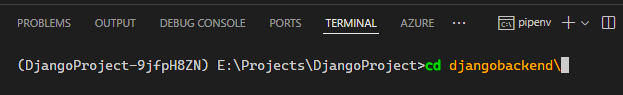
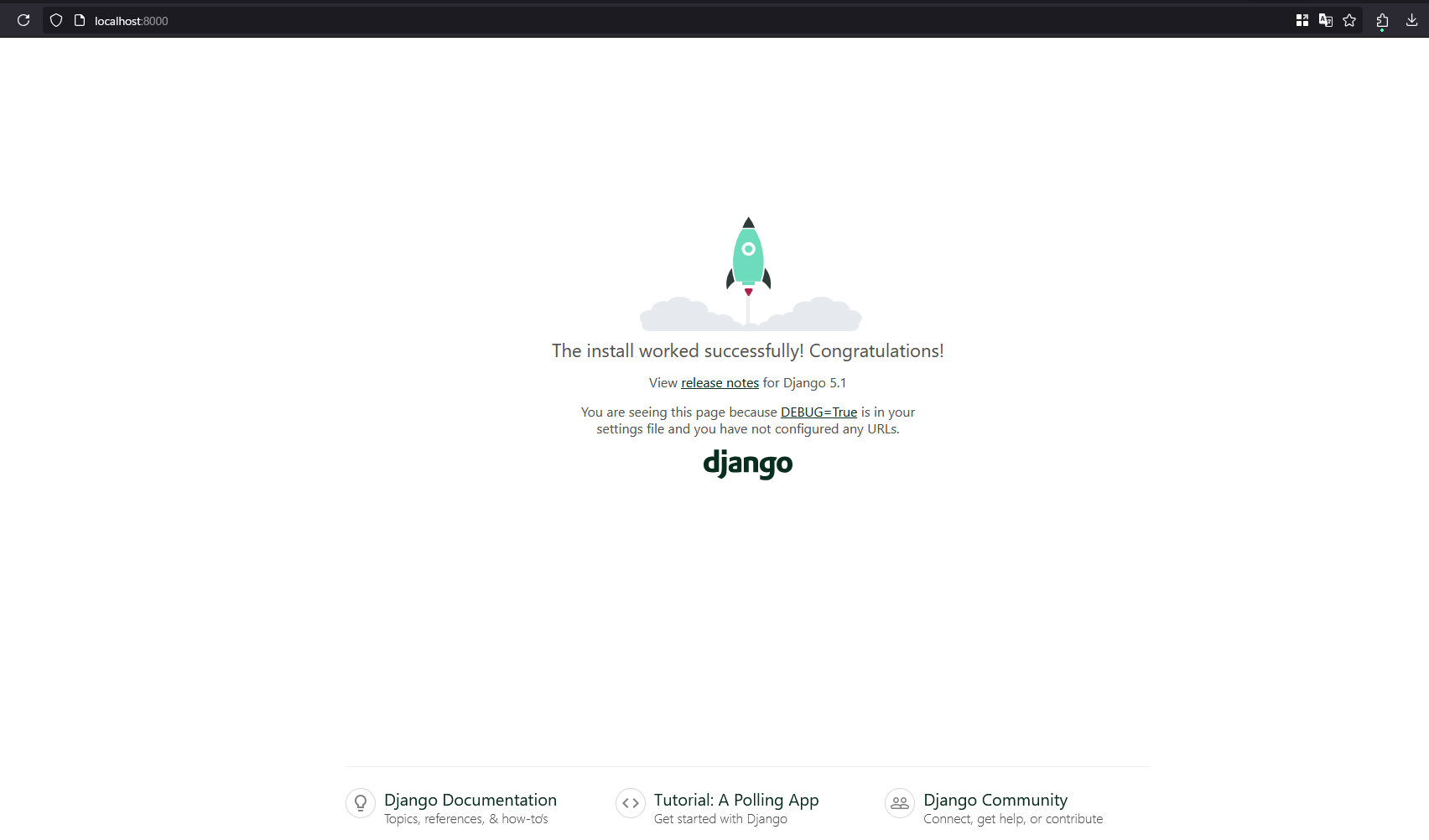
Once that's done, run the command python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 to start your Django project
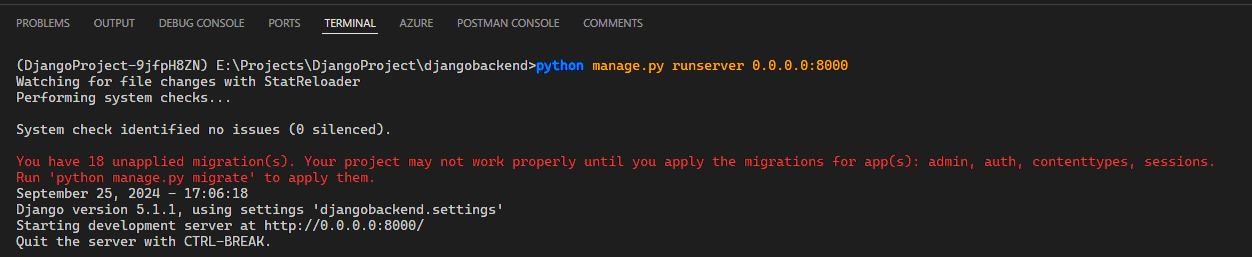
Your Django project will now be visible on the URL https://localhost:8000
Up Next: 3 - Project Structure